TRICARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Agaric acid, also known as agaricin (2-hydroxynonadecane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid) has a mono-hydroxylated C22 saturated carbon chain with 3 carboxyl groups. It is found in fungi, e.g. Laricifomes officinalis. It is an inhibitor of several metabolic steps as it prevents the formation of C2 units from citrate and reduces the availability of citrate for the activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and it induces the mitochondrial permeability transition by collaborating with adenine nucleotide translocase (Chávez E et al., Biochem Res Int 2020, 5253108). Agaric acid is used in medicine as an anhidrotic agent in order to stop excessive cutaneous perspiration.
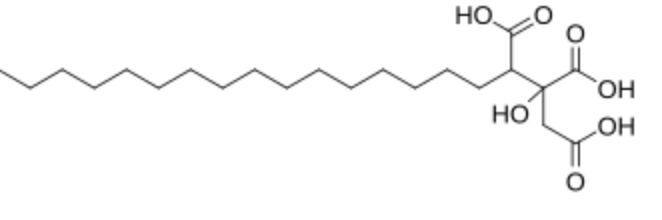 Agaric acid
Agaric acid
Bongkrek acid (also known as bongkrekic acid) has a C24 unsaturated carbon chain (7 double bonds) with 3 carboxyl groups, 3 methyl groups and one methoxy group. In 1895, there was a food-poisoning outbreak in Java caused by the consumption of Indonesian traditional food called tempe Bongkrek. Dutch scientists, W.K Mertens and A.G. van Veen identified in the early 1930s the source of poisoning as a bacterium called Pseudomonas cocovenenans. This bacterium, which is also named Burkholderia cocovenenans, is the source of a poisonous substance called Bongkrek acid. Its first total synthesis was made by E.J. Corey in 198 (Wikipedia). Later, it has been found that bongkrek acid works in interrupting the transport process of the cytosolic ADP in the inner membrane of mitochondria by inhibiting the mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocator,.
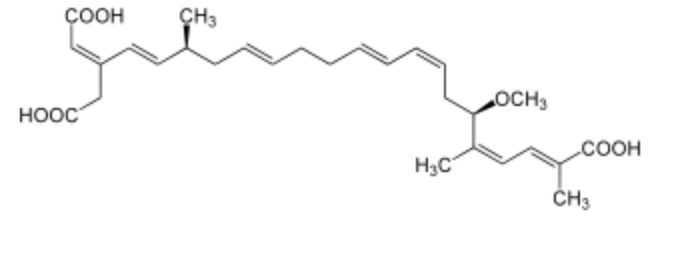
Bongkrek acid
DISPERSIVE LIQUID-LIQUID MICROEXTRACTION
Lire la suiteDevenez membre et participez au développement de la Lipidomique au XXIème siècle.
S'inscrire