Neutral lipids fractionation
Several procedures are proposed below and the analyst must choose that which seems the most appropriate for a given extract and the specific aim of the research. The separation of neutral lipids is only a part of complex recipes which are described to separate all kinds of lipids, the analyst may thus choose only the part adapted for his problem in running the procedure from the beginning to the specific step.
The same silica gel column as described before for the separation of all lipid classes may be adapted for the separation of the different neutral lipid fractions of a complex lipid extract. The step-elution is made according to Ingalls ST et al. (J Chromatogr 1993, 619, 9).
Apparatus:
The same as previously described (general procedure): small glass columns or SPE cartridges.
Reagents:
Silica gel 60 (230-400 mesh) suspended in isooctane
Isooctane (trimethyl-2,2,4-pentane), ethyl acetate, acetic acid
Procedure:
Prepare the column as previously described but with isooctane instead of chloroform.
Wash the column with 2 ml of isooctane/ethyl acetate (80/1, v/v) and transfer the lipid sample dissolved in 0.5 ml of the same solvent. Wash the vial with another 0.5 ml and pour on the column.
1- Add 5 ml of the same solvent, this will elute cholesterol esters.
2- Add 5 ml of isooctane/ethyl acetate (20/1, v/v), this will elute triglycerides.
3- Rinse the lipid vial with 2 x 0.5 ml of isooctane/ethyl acetate (75/25, v/v) and pour on the column. Add 5 ml of the same solvent mixture, this will elute cholesterol and diacylglycerols.
4- Add 5 ml of isooctane/ethyl acetate/acetic acid (75/25/2, v/v), this will elute the free fatty acids.
5- After rinsing the lipid vial with 2 x 0.5 ml methanol and pouring the solution on the column, phospholipids can be eluted with 20 ml methanol.
Comments:
1- The purification of ceramides is efficiently processed by elution with 5 ml of chloroform/methanol (95/5, v/v) after the elution of the other neutral lipids with pure chloroform. The acylglycosylceramides (and some monogalactosyl diglycerides) are also present in the ceramide fraction. The glycolipids are eluted as previously described or more efficiently with 10 ml of chloroform/acetone (1/1, v/v) followed by 10 ml pure acetone.
2- To prepare a pure fatty acid fraction, the silica column is first equilibrated with isooctane/ethyl acetate (75/25, v/v), the sample is applied to the column in the same solvent. True neutral lipids are eluted by 5 ml of the same mixture and free fatty acids are eluted by 5 ml of isooctane/ethyl acetate/acetic acid (75/25/2, v/v).
3- When analyses of low (trace) levels of fatty acids or other compounds are planned after neutral lipid fractionation, it is recommended to wash the silica gel before use by 3 successive suspensions and decantation in pure methanol followed by desiccation under vacuum lands drying at 110°C. Keep the washed silica gel in a tightly closed vessel.
An aminopropyl cartridge has been proposed with success to fractionate complex lipid extracts into various neutral lipids and sphingolipid classes (Bodennec J et al. J Lipid Res 2000, 41, 1524). The following procedure may be used to efficiently separate ceramides from the other neutral lipids (except monoglycerides), fatty acids but also complex sphingolipids (sphingomyelin and glycosphingolipids). A preliminary alkaline treatment removing glycerolipids is useful if a pure ceramide fraction (and a pure glycosphingolipid fraction) must be prepared.
Apparatus :
Aminopropyl-bonded silica gel cartridges (500 mg matrix) from Supelco or Macherey-Nagel.
Reagents :
chloroform, methanol, ethyl acetate, hexane, diisopropyl ether, acetic acid, acetone, ammonium acetate
Procedure :
– SPE cartridges are washed with 5 ml hexane before loading with the lipid extract (up to 15 mg lipids in 200 ml chloroform)
– wash with 2 ml of hexane/ethyl acetate (85/15, v/v) to elute neutral lipids if present (cholesterol esters, triglycerides, fatty alcohol, cholesterol, diacylglycerols)
– wash with 4 ml of chloroform/methanol (23/1, v/v) to elute free ceramides, monoglycerides and some sphingoid bases
– wash with 3 ml diisopropyl ether/acetic acid (98/5) to elute free fatty acids
– wash with 10 ml of acetone/methanol (9/1.35) to elute neutral glycosphingolipids and sphingoid bases
– wash with 4 ml of chloroform/methanol (2/1, v/v) to elute sphingomyelin
– wash with 4 ml of chloroform/methanol/3.6 M ammonium acetate (30/60/8, v/v) to elute sulfatides, sphingosine phosphate and ceramide phosphate)
Another procedure using the same solvents and column has been described for neutral lipids (Giacometti J et al., J Chromatogr A 2002, 976, 47). In that work, the lipids are loaded as chloroform solution, steryl esters are eluted with 5 ml of hexane, triglycerides with 5 ml of hexane/methanol/chloroform (88/10/2, v/v), sterols with 5 ml of hexane/ethyl acetate (5/95, v/v), diglycerides with 5 ml of hexane/ethyl acetate (15/85, v/v), and monoglycerides with 5 ml of chloroform/methanol (2/1, v/v).
Separation of free fatty acids from bound fatty acids (triglycerides and phospholipids) in lipid extracts may be achieved using bonded phase aminopropyl-silica cartridges conditioned with chloroform (3 ml) (Lacaze JP et al., J Chromatogr A 2007, 1145, 51). The lipid extract in chloroform (0.5 ml) is loaded onto the cartridge. The cartridge is washed with 1 ml of chloroform/2-propanol (2/1, v/v) and the free fatty acids are eluted with 3 ml of diethyl ether/acetic acid (98/2, v/v).
Below is described an efficient procedure to isolate quite all neutral lipid fractions of a complex lipid mixture.
Apparatus:
The same as previously described (general procedure)
Reagents:
Silica gel 60 (230-400 mesh)
Hexane, diethyl ether
Procedure:
– The neutral lipids are dissolved in 1 ml hexane and poured on a column of silica gel prepared in hexane.
– Add 3 ml of hexane, this will elute hydrocarbons and squalene.
– Add 6 ml of hexane/diethyl ether (99/1, v/v), this will elute sterol esters, waxes and fatty methyl esters.
– Add 5 ml of hexane/diethyl ether (95/5, v/v), this will elute triglycerides, alkyl and alkenyl acylglycerols and tocopherols.
– Add 5 ml of hexane/diethyl ether (92/8, v/v), this will elute free fatty acids and fatty alcohols.
– Add 8 ml of hexane/diethyl ether (85/15, v/v), this will elute cholesterol and diglycerides.
– Add 5 ml diethyl ether to elute some diglycerides and monoglycerides.
An efficient procedure to isolate in pure form some groups of neutral lipids is described below. The fractions may be further analyzed by thin-layer chromatography or HPLC.
Reagents:
Silica gel 60 (230-400 mesh)
chloroform, hexane and diethyl ether
Procedure:
The neutral lipid fraction is first isolated according to the general procedure on a silica gel but after elution with acidified chloroform.
The evaporated lipid extract is dissolved in hexane and poured on the column previously equilibrated in the same solvent.
– elute with 3 volumes of hexane, this purifies hydrocarbons including squalene
– elute with 6 volumes of hexane/diethyl ether (99/1, v/v), this purifies sterol esters, fatty acid methyl esters and waxes
– elute with 5 volumes of hexane/diethyl ether (95/5, v/v), this purifies triglycerides, alkyl and alkenyl acylglycerols and tocopherols
– elute with 5 volumes of hexane/diethyl ether (92/8, v/v), this purifies free fatty acids and fatty alcohols
– elute with 8 volumes of hexane/diethyl ether (85/15, v/v), this purifies cholesterol and a part of the diacylglycerols
– elute with 5 volumes of pure diethyl ether, this purifies monoacylglycerols and the rest of the diacylglycerols.
In several laboratories this technique was used to prepare hundred mg of lipids from natural sources. Although peaks may contain more than one compound, the major neutral lipid classes can be separated on silicic acid columns and later, purified by TLC. We give below the elution profile obtained with a column filled with 20 g of adsorbent (dimensions: 1 x 40 cm), 10 ml fractions were collected.
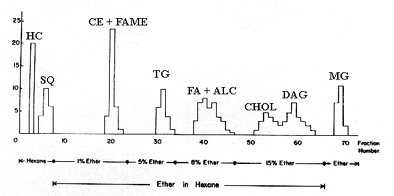
HC: hydrocarbon, SQ: squalene, CE: cholesterol esters, FAME: fatty acid methyl esters, TG: triacylglycerols, FA: fatty acids, ALC: fatty alcohols, CHOL: cholesterol, DAG: diacylglycerols, MG: monoacylglycerols.
Comments:
A method utilizing aminopropyl bonded phase (Bond Elut, Analytichem International) columns has been proposed to separate lipid mixtures into individual classes of neutral lipids (free fatty acids, cholesterol esters, triglycerides, diglycerides, monoglycerides and cholesterol) and one phospholipid class (Kaluzny MA et al J Lipid Res 1985, 26, 135).
Although this method appeared difficult to manage in our hands, it may be adapted to various materials with some effort but affords rapid and convenient separations of several samples in one process with the described collector rack.
A modification of the Kaluzny procedure adapted more precisely for ceramides and glycosphingolipids (in the presence of neutral lipids) is reported above (second procedure).
DISPERSIVE LIQUID-LIQUID MICROEXTRACTION
Lire la suiteDevenez membre et participez au développement de la Lipidomique au XXIème siècle.
S'inscrire