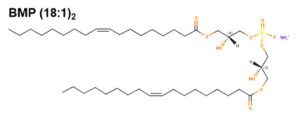
This curious phospholipid known also as bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate has a stereochemical configuration, 3-acyl-sn-glycero-1-phosphoryl-1′-sn-[3′-acylglycerol], different from that of all the other known mammalian phospholipids, that have the sn-glycero-3-phosphoryl configuration (Brotherus J et al., Chem Phys Lipids 1974, 13, 178). This phospholipid is an acidic phospholipid and a structural isomer of phosphatidylglycerol, consisting of lysophosphatidylglycerol with an additional fatty acid esterified to the glycerol head group. It is thought to be synthesized from phosphatidylglycerol in the endosomal/lysosomal compartment and is found primarily in multivesicular bodies within the same compartment.
This phospholipid was first identified in the lung of mammals (Body DR et al., Chem Phys Lipids 1967, 1, 254) and was later shown to be enriched in lysosomes of rat liver (Wherrett JR et al., J Biol Chem 1972, 247, 4114). Its accumulation was demonstrated in the lysosomal compartment, especially during some lysosomal storage disorders (Niemann-Pick diseases, neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses) and drug-induced phospholipidosis. Its involvement in both dynamics and lipid/protein sorting functions of late endosomes has started to be documented, especially in the control of cellular cholesterol distribution (Hullin-Matsuda F et al., Prost Leukotr Essent Fatty Acids 2009, 81, 313). Investigations in animals with gangliosidoses have shown that the content of bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate in brain was significantly greater in humans and in animals with either GM1 or GM2 ganglioside storage diseases, than in brains of normal subjects (Akgoc Z et al., J Lipid Res 2015, 56, 1006). C22:6, C18:0, and C18:1 were the predominant fatty acids in gangliosidosis brains.
There is a rise in bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate-related publications, reflecting the increasing recognition of the functional importance of this phospholipid in membrane biology (Review in: Showalter MR et al., Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21: 8067).
In addition, R1 or R2 are frequently arachidonic acid (alveolar macrophages) or docosahexaenoic acid in some other cells (Holbrook PG et al., Biochim Biophys Acta 1992, 1125, 330), oleic acid being the other acyl group.
More recently, it was shown that lysobisphosphatidic acid is a major phospholipid, with phosphatidylcholine, in the late endosomes (Kobayashi T et al., J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 32157). It was also found that lysobisphosphatidic acid exhibited unique pH-dependent fusogenic properties, thus, this lipid is an ideal candidate to regulate the dynamic properties of these cellular membranes.
It was reported that lysobisphosphatidic acid containing two 22:6n-3 may be a marker of drug-induced phospholipidosis (Baronas ET et al., Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2007, 218, 72). Initially, its level was shown to account for 21% of the increase in phospholipids in a rat model of phospholipidosis (Cox JW et al., Biochem Pharmacol 1989,38, 3535). The relationship between phospholipid metabolism and drug-induced toxicity remains enigmatic.
This unusual phospholipid has also been described in various obligatory and facultatively alkalophilic Bacillus strains (Clejan S et al., J Bacteriol 1986, 168, 334).
An alanyl derivative of bis(acylglycerol)phosphate was isolated from various bacteria and characterized (Fisher W et al., J Bacteriol 1998, 180, 2093).
DISPERSIVE LIQUID-LIQUID MICROEXTRACTION
Lire la suiteDevenez membre et participez au développement de la Lipidomique au XXIème siècle.
S'inscrire