These fatty acid derivatives may be considered as complex lipids since they are formed of one fatty acid, a 3′-phospho-AMP linked to phosphorylated pantothenic acid (vitamin F) and cysteamine. However, to simplify the nomenclature and taking into account their metabolism, we classify them within the big group of the fatty acids and their simple derivatives rather than within the complex and phosphorylated lipids.
Long-chain acyl-CoA esters are substrates for a number of important enzymatic reactions and play a central role in the regulation of metabolism as allosteric regulators of several enzymes. To participate in specific metabolic processes, fatty acids must first be activated by being joined in thioester linkage (R-CO-SCoA) to the -SH group of coenzyme A. The thioester bond is a high energy bond.
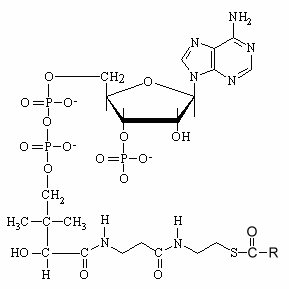
R = fatty carbon chain
The activation reaction normally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum or the outer mitochondrial membrane. This is an ATP-requiring reaction (fatty acyl-CoA synthase), yielding AMP and pyrophosphate (PPi). Different enzymes are specific for fatty acids of different chain length.
Then, the acyl CoA esters are transported in mitochondria. They are converted to fatty acyl carnitine by carnitine acyl transferase I, an enzyme of the inner leaflet of the outer mitochondrial membrane. Fatty acyl carnitine is then transported by an antiport in exchange for free carnitine to the inner surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane. There carnitine acyl transferase II reverses the process, producing fatty acyl-CoA and carnitine. This shuttle mechanism is required only for longer chain fatty acids.
Once inside the mitochondrial matrix, the fatty acyl-CoA derivatives are degraded by a series of reactions that release acetyl-CoA and leads to the production of NADH and FADH2. There are four steps in fatty acid oxidation pathway; oxidation, hydration, oxidation, and thiolysis. It requires 7 rounds of this pathway to degrade palmitate (a C16 fatty acid).
A graphic chart of these important metabolic steps may be found in the BioCarta web site.
Devenez membre et participez au développement de la Lipidomique au XXIème siècle.
S'inscrire